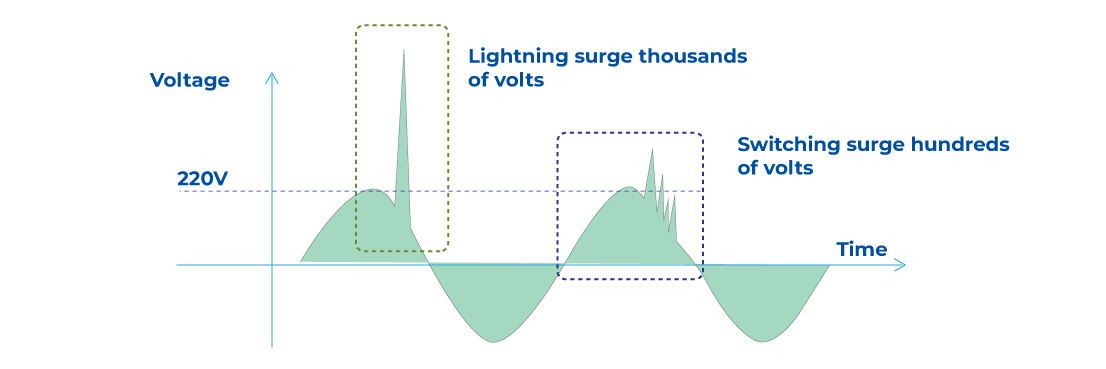
When we examine the causes of surge voltages, we can list them as follows:
- Lightning strikes,
- Faults originating from the power grid,
- Commissioning problems,
- Surges caused by switching components,
- Temporary voltage fluctuations,
- Harmonics,
- Voltage dips.
The distinct characteristic of these types of surges is that they are short-lived but occur repeatedly. This is why additional protective products are needed to safeguard electrical devices in the system. While fuses and relays operate during long-term surges, the necessity for additional protective devices to be included in every panel or product, similar to a fuse, becomes evident.
Products such as motor control units, welding machines, switching components, and industrial devices, which cause sudden power interruptions, grid faults, or sudden voltage fluctuations in the grid, may not damage electrical devices at once. However, they create small stresses that lead to permanent damage over time, gradually wearing down these products.
Protective devices absorb the energy of these surge voltages, preventing devices from being damaged. This ensures service continuity and reduces the repair costs of critical devices in the system.
Devices that have been in operation for a long time frequently fail due to surge-related issues, leading to damages that are not covered under warranty. To prevent such costs, the use of protective devices can avoid the emergence of more significant expenses.